Water is essential for not only the health, wellbeing, and livelihoods of human populations, but also the plants and animals that share our planet.
Our WaterRA research projects in Health and Environmental Impacts study the role that changing physical, biological, and chemical characteristics of water (such as quality and quantity) plays in the health of people, plants, animals, and the aquatic environments in which they live. This may include projects that look at contaminant sources and their impacts, such as the use of pesticides, mining, run-off, incineration, domestic chemicals, industrial pollution, etc.
Working together with our members, our projects provide important evidence to support the maintenance of healthy waterways, habitats, and ecosystems in order to preserve and enhance our natural environment and foster thriving communities and liveable cities.
Featured project
Cryptosporidium is a waterborne microscopic parasite with different forms at various stages of its lifecycle…
Related projects
Contaminants of emerging concern (CECs) pose a potential risk to human health and the environment…
During the SARS-CoV-2 global pandemic, the Victorian Department of Health developed the most comprehensive and extensive program of sewage surveillance in Australia…
With Australia’s annual average temperatures increasing, evidence shows that a warming-induced increase in carbon dioxide (CO2) released from soils leads to a rise in the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere…

Climate change is increasing the risk of more frequent, more intense, and more widespread bushfires…

This project is being driven by the need for water utilities and regulators to have up-to-date and peer-reviewed information on the pathogen risk associated with different animals being found in treated treated water assets or storage tanks…

Xenobiotic compounds such as perfluoroalky substances have been plaguing our ecosystem by entering our food and water supplies…

To improve water security, drought and environmental resilience of our water bodies many utilities and governments are exploring ways to augment natural systems with highly treated recycled water (HTRW)…

As we are becoming more and more aware of the large number of organic micropollutants in the aquatic environment…

Wastewater treatment is a procedure used to remove contaminants from wastewater and reduce the levels of pathogenic microorganisms present in human waste…

Research into Contaminants of Emerging Concern (CECs) forms the basis of ensuring ecosystem health for the enjoyment of future generations…

The aim of this project is to determine which physical features of textiles increase fibre release during washing, so they can be reengineered to minimise environmental impacts, improving the quality of bioresources such as effluent water and biosolids…

Biosolids generated during the wastewater treatment processes has become a major burden of wastewater treatment plants and an unresolved problem for major cities around the world…

The project aims to investigate the impacts of biosolids biochar immobilized bacteria on soil microbial activity and diversity during arsenic phytoremediation…

Energy sector focusses to be able to meet all the requirements of sustainable national development of energy resources and efficient utilization of its diverse sources…

The main aim of this research project is to evaluate the agricultural potential of struvite as a sustainable phosphorus fertiliser…

Influence of sampling methods on the production of volatile emissions from biosolids-related sources
As there is lack of understanding the roles of sampling methods on measuring for volatile gas sampling from biosolids, it might cause various concern about what are we really measuring…

In Australia, around 1.4 million tonnes of biosolids were produced in 2021…

The aim of this project is to identify environmental and public health risks associated with urban wetland sediment from recreational activities undertaken in or around urban wetlands across Melbourne…

The biosolids industry in Australia has historically developed in response to the regional challenges, resources available and their markets perception and demands…

Biosolids odour impacts communities and public perception of water utilities…
The occurrence of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAs) in various environmental media is of great concern due to their potential adverse effects on living organisms…
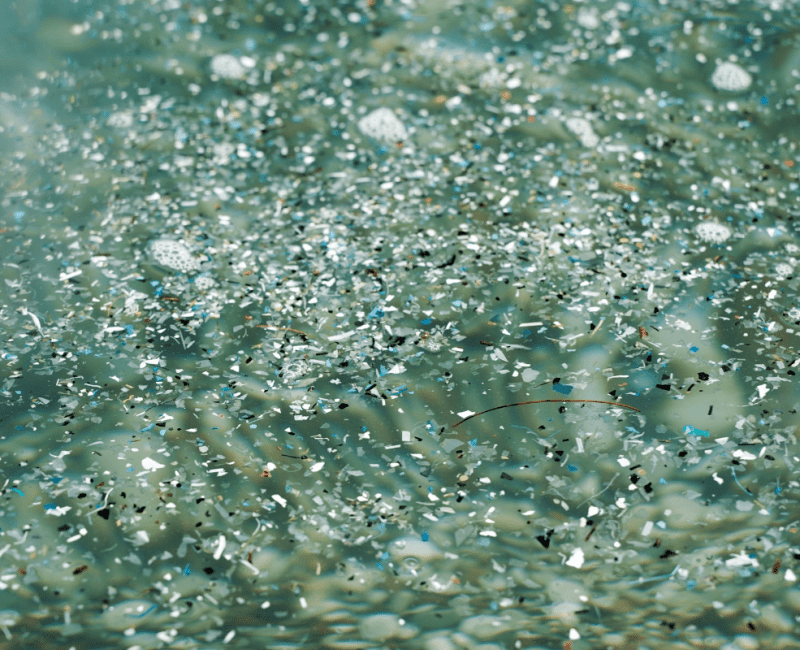

This project is investigating the fate and transport of microplastics in the whole of water supply cycle…

The genus Microcystis is responsible for many ‘nuisance’ and toxic algal blooms that threaten various fresh water bodies in Australia…

This project investigated Metabolomics-based applications (LC-MS and GC-MS) to advance cyanobacterial toxin detection and analysis in water to…
Viruses are responsible for more than 50% of all health-care associated gastroenteritis…
This project determined disinfection by product contribution from chlorination of algae…

This research identified and validated the impacts of particle-pathogen association on the disinfection of various microorganisms in the treated wastewater effluents…
This project improved the knowledge of how algae species (population density, morphology and AOM concentration and character) and coagulation conditions (coagulant type, pH, polymer dose, and shear) impact algal floc properties in order to improve the C-F process and downstream separation treatment…

This project aimed to predict the fate and removal of micropollutants during wastewater treatment by the application of fugacity modelling…

Biosolids and other porous organic materials are susceptible to self-heating when stockpiled…

This project developed analytical methods to study the speciation of inorganic and organic chloramines…

Sunlight-induced degradation is an important removal mechanism for some contaminants and has been commonly overlooked as a removal mechanism in wastewater systems in the past…
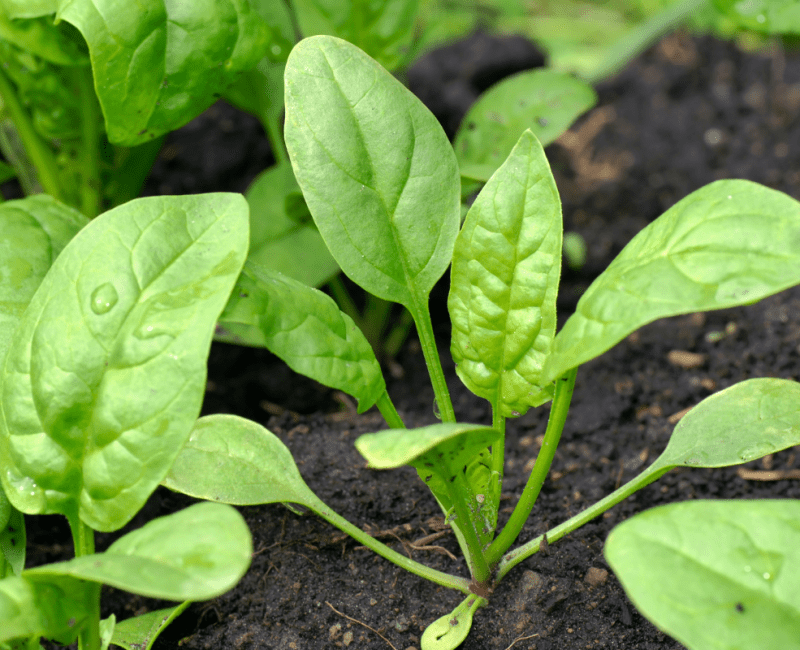

This study examined seedling emergence and early development growth responses of Spinacia oleracea L. (spinach) in per and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) contaminated soil…
This study successfully developed a variety of specific qPCR assays for the characterisation of host faecal contamination…

This research investigated the impact of recycled water runoff entering the Tilligerry Creek and broader Port Stephens estuary…

Microbeads derived from personal care products that are introduced to waste water treatment streams and contaminated by persistent organic pollutants are an increasing area of concern for terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems…

Intertidal marine environments are highly valued for their ecosystem services, yet it is often unclear whether productivity within sandy beaches and rocky shores is driven by nutrients derived from terrestrial, marine or in situ sources…

Soil hydrophobicity is reported to vary under different vegetation types, and in different soil environments (e.g. pH, soil texture, total organic carbon, and microbial activity)…
This research investigated the impact of failing on-site septic systems and agricultural runoff entering the Tilligerry Creek and broader Port Stephens estuary…
This research investigated the impact of failing on-site septic systems and agricultural runoff entering the Tilligerry Creek and boader Port Stephens estuary…

The presence of taste and odour (T&O) is a growing concern for the water industry due to negative associations with unsafe drinking water…

Radionuclides are used for nuclear medicine, veterinary medicine, and research purposes…

Cryptosporidium is a protozoan parasite that causes the diarrhoeal disease cryptosporidiosis…

The increasing use of engineered nanomaterials (ENMs) in consumer products has created concern about their fate and effect in the environment…

This project revised operational methodologies in all systems from catchment to tap providing an improved understanding of the resource and cost implications…

This project developed and tested novel instrument components used in the construction of a portable, robust and inexpensive flow injection analysis (FIA) system for the detection of triazine herbicides using chemiluminescence (CL)…

There are over 40,000 chemical compounds registered for use in Australia; however, very few of these have been monitored in aquatic receiving environments…

This research considered whether urban water governance, environmental regulation and recreational water quality management impact decisions to either reuse urban wastewater or dispose of it to the environment, and identifies opportunities for reform…

This project investigated the relationship between disinfection by-product (DBP) formation in drinking water and the molecular weight distribution of its natural organic matter precursors (NOM) to help increase our understanding of how NOM properties such as size, aromaticity and structure affect DBP formation and toxicity of the formed DBPs…

This project characterised the acute cytotoxicity of a hydraulic fracturing fluid using a human gastrointestinal cell line and, using this data, contribute to the understanding of potential human health risks posed by Coal Seam Gas (CSG) extraction in Queensland…

Anabaena circinalis, is a commonly occurring cyanobacterial species in Australian source waters…

This project investigated the effect of environmental parameters on the regulation of cylindrospermopsin biosynthesis in cyanobacteria inhabiting Australian drinking water supplies….

Remote communities have an issue with hardness levels in water supplies…

Following the discovery of a species of cyanobacteria displaying novel toxicity, Limnothrix as a cause for concern, this project identified the toxin and developed techniques to detect and isolate it…

This project developed more sophisticated ways in which to study dissolved organic matter (DOM) from a variety of different water sources (wastewater, dam water etc)…
This project provided an on-line monitoring protocol utilizing fluorescence to aid utilities in their provision of safe drinking water thus addressing the National Research Priority Goal “Water – A critical resource”…
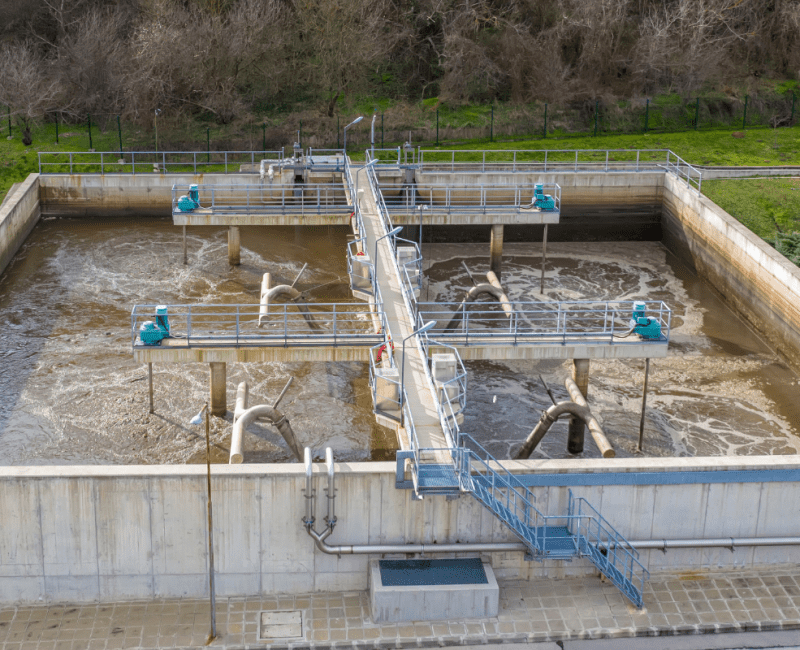
This project investigated the impact of hazardous events (i.e. high organic, high salinity, high toxic shock loads in influent, aeration lost or membrane damage) on decentralised membrane bioreactor performance…
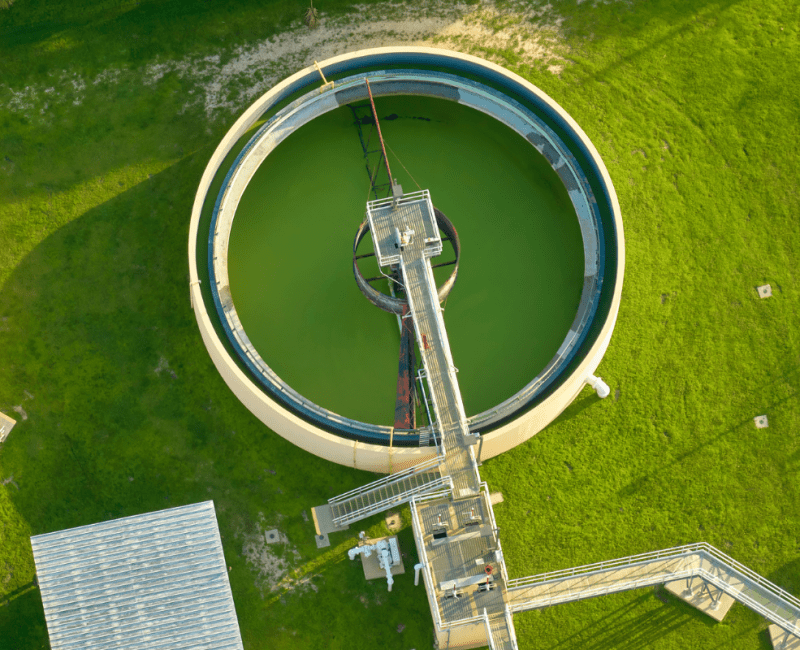
This project developed an understanding of the occurrence of regulated and emerging disinfection by-products (DBPs) in drinking water in Southeast Queensland (SEQ)…

This project addressed the removal rate of ammonia by microorganisms and designed a pathogen survey to establish the level of contaminants present within influent water at the Aquifer storage and recovery site at the Aldinga Aquifer…

This project identified the promising biomarkers shown to be capable for distinguishing between infectious and non-infectious Cryptosporidium oocysts as well as identify species that can/cannot infect humans…

This project increased understanding of how cyanobacteria adapt and function in today’s environment…

This project established a bioassay using mouse embryonic stem cells to assess the effects of the cyanobacterial toxin, cylindrospermopsin, on early embryonic development…

This project investigated the preparation and stability of concentrated preformed monochloramine solutions, with the potential application of remote area redosing to maintain disinfectant residual…

This project determined the decay rates of E. coli, S. typhimurium, bacteriophage (MS2) and adenovirus in biosolids-amended soil used in agriculture…
Faecal source tracking (FST) involves the identifying the contamination pathways and potential health risk of faecal contamination in source waters and is an important strategy for contaminant management within catchments…
Wastewater surveillance has played a key role in supporting the public health responses to the COVID-19 pandemic, including throughout Victoria, Australia…

Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) – the ability of microorganisms to resist antibiotics, antifungals, and antivirals – is one of the greatest health threats of the 21st century…

WaterRA is leading a consortium of water industries as part of the future configuration of the “CRC Care” post-June 2021…
This project aims to better understand chemical and biological hazards in Australia through long-term collection and analysis of wastewater and biosolids…
Biochar production from pyrolysis/gasification and its use as increasing soil carbon has been discussed as one of the most suitable low emissions technologies..

Wastewater is known to contain tiny particles of plastic, some may remain at the end of the treatment process…

Water Footprinting provides a different approach to understanding the role of water than traditional water resources planning and management.

The protozoan parasites, Cryptosporidium and Giardia represent a major public health concern of water utilities in developed nations…

This project formed the Mekong node of the Collaboration on Sewage Surveillance for SARS-CoV-2 “ColoSSoS” project after Water Research Australia and the Australian Water Association identified that technology transfer within Australia’s broader region was a logical extension of the local project…

Following on from the successes of the Mekong node of the ColoSSoS program, WaterRA entered into another project with the Australian Water Association to provide knowledge transfer and capacity building services to the Water Authority of Fiji…
The Collaboration on Sewage Surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 (ColoSSoS) project combined the expertise of more than 50 Australian organisations in R&D activities that have enabled health departments across the country to integrate quantitative measurements of SARS-CoV-2 virus detected in sewage with human clinical PCR test data for COVID-19…
This project aims to understand and reduce the spread of antibiotic resistance in disinfection…

The Collaboration on Sewage Surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 (ColoSSoS) project combined the expertise of more than 50 Australian organisations in R&D activities that have enabled health departments across the country to integrate quantitative measurements of SARS-CoV-2 virus detected in sewage with human clinical PCR test data for COVID-19…
There are many species of blue-green algae (cyanobacteria), and each species can have a number of genotypes…
Several cyanobacteria species are well known for their potential to produce cyanotoxins…

Wastewater must be treated to remove four classes of pollutants to levels that regulators consider safe for discharge to the environment: these are nutrients, micropollutants, total suspended solids and pathogens..

People excrete antibiotics and many types of bacteria, and this mixture can become concentrated in wastewater treatment plants…

The water industry needed a clear and consistent approach to assess the efficacy and performance of the many technologies for managing algal blooms in waterbodies…

The standards for recycling stormwater are higher for drinking water than for non-potable reuse such as agricultural or urban irrigation…

Micropollutants, mixtures and transformation products in recycled water: How much do we really know?
Recycled water usually contains extremely low levels of many different chemicals…

In 2006, strict restrictions on using tap water for gardening or car-washing were imposed in Melbourne but relaxed in 2010-2011 as rainfall replenished depleted reservoirs…
Wastewater often contains endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs) such as ethinyl estradiol (EE2) which is excreted by women who use some oral contraceptive pills…

There are concerns that recycled wastewater used for watering gardens or washing cars might be accidently ingested…
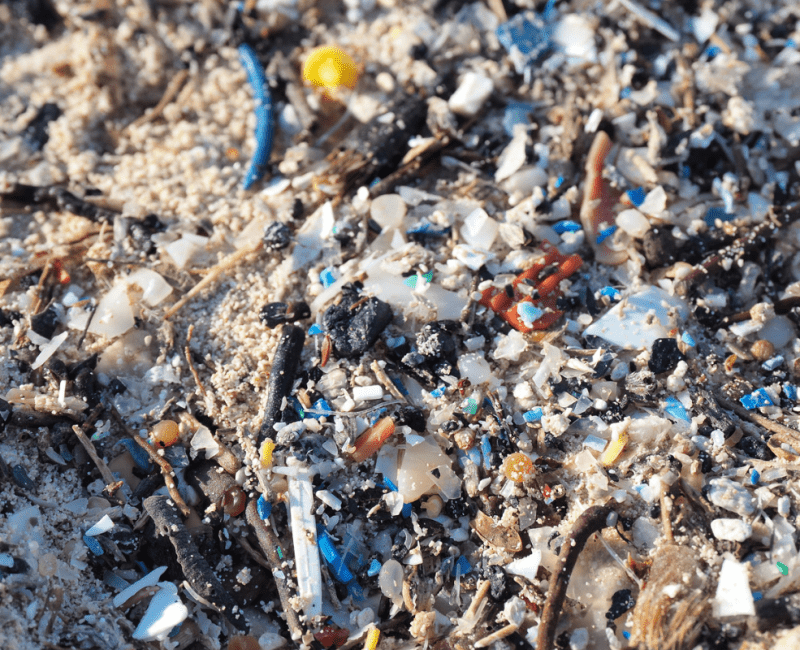

Microplastics are already somewhat ubiquitous in the environment, due to the wide use of plastics around the world…

Water Research Australia led an innovative, and collaborative Australia-wide investigation that developed novel methods for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater…

Wastewater recycling uses reverse osmosis (RO) membranes to produce freshwater but this process also generates a waste stream – the reverse osmosis concentrate (ROC) – which contains almost all the contaminants present in the original wastewater…

Membranes are used to remove viruses from treated wastewater to make it safe for discharge or recycling…

Smaller and regional Wastewater Treatment Plants (WWTPs) have the capacity to recycle wastewater for agricultural use, but the cost of obtaining regulatory approval or ‘accreditation’ is prohibitive…

Fish, frogs, and other aquatic animals sometimes show signs of ‘endocrine disruption’; aberrant changes to their hormone or reproductive systems that are thought to be caused by chemicals in the water they inhabit..

Ultrafiltration membranes are used to remove viruses from treated wastewater…

Some wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) use membrane bioreactors (MBR)…

The Australian water industry uses a variety of membrane processes to remove unwanted pathogens or compounds, such as salt, from source waters…

Wastewater must be treated to remove harmful pathogens and chemicals before it can be released to the environment, but the cost of proving that all pollutants have been removed is prohibitive because potentially thousands of separate chemicals would have to be measured…

Wastewater (WW) contains harmful chemicals, including pesticides, that can disrupt normal gene function or hormone activity…

The ADWG explains policies but does not provide the specific steps and actions needed to apply risk management principles within a water treatment plant (WTP)…
Burkholderia pseudomallei is a bacteria that is widespread in SE Asia and northern Australia, where there are an average of 16 cases per 100,000 people…

European carp have decimated native fish species in the Murray-Darling River…

Microbial pathogens are removed from source waters to make safe drinking water. Health-based targets (HBTs) refer to the quantities of pathogens that will NOT cause illness, and water treatment plants (WTPs) must ensure that the numbers of pathogens in potable water are the same or lower than the HBTs…

Before treated wastewater can be discharged to the environment, utilities are required to perform a direct toxicity assessment (DTA), which usually requires that live aquatic animals, such as fish, swim in the clean discharge water for 4-10 days while their growth and activity are observed and measured…
E. coli bacteria naturally populate the gastrointestinal tract of humans and animals; they are usually harmless and are commonly excreted…

Water treatment plants (WTP) produce safe drinking water that does not contain harmful microscopic pathogens, but subsequent pipe-leaks or valve or hydrant malfunctions en route to the customers tap increase the risk of pathogens entering the public water supply…

Although a cluster of customer complaints can identify specific water quality issues such as a dirty water event, it is more difficult to understand the extent of general customer satisfaction with water quality and taste…

The ADWG has methods for predicting risks to water quality, but these were not developed for managing extreme climate-change driven weather events such as bushfires or floods…

This research was prompted by concerns that rooftop-harvested rainwater fed into household hot water services might expose the public to harmful pathogens such as salmonella…

‘Microbial source tracking’ (MST) is a technique that aims to identify the animal that excreted faeces and polluted water…
Cryptosporidium, a microscopic pathogen, forms infectious oocysts which are removed by specific and targeted water treatments…
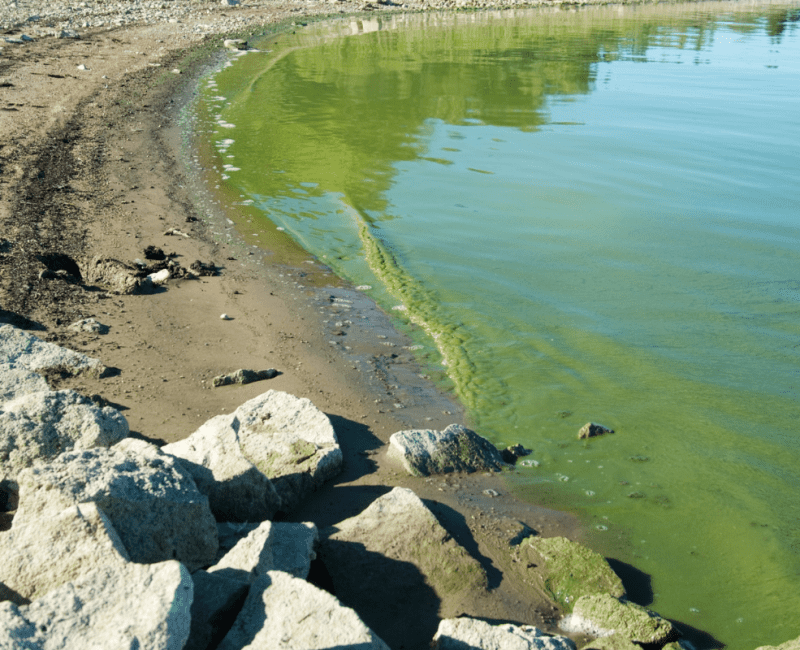

Blue-green algae (cyanobacteria) blooms decrease water quality by releasing toxins and unpalatable taste and odour compounds…

The ADWG 2011 lacked objective, quantifiable criteria for measuring pathogen removal from source waters…

Climate change is depleting water resources, while population increases drive demand for additional recreational facilities, particularly in the vicinity of urban centres…

Approximately 11% of Australians use rainwater as their main source of potable water but this poses a potential health risk caused by chemical contaminants or microbial pathogens from birds or mammals being washed off the roof…
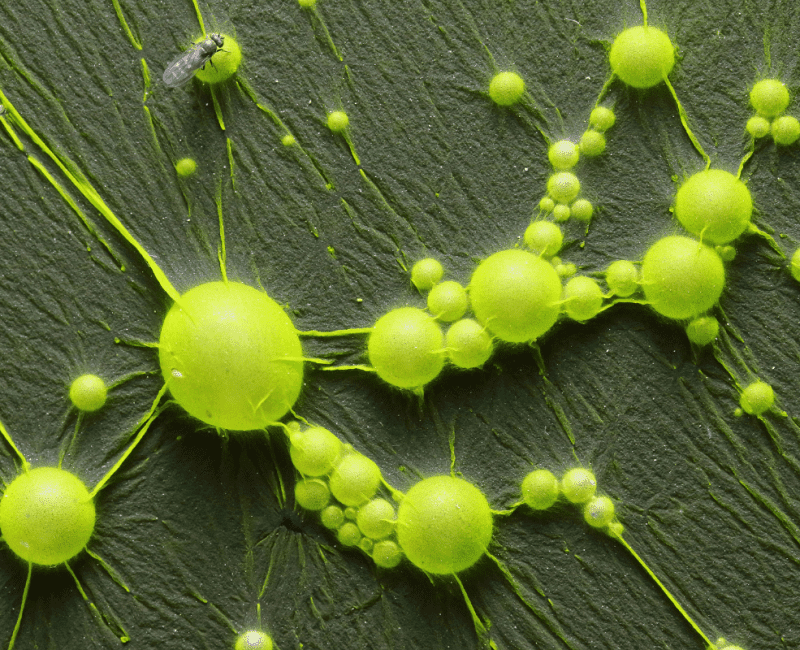

Cyanobacteria are blue-green algae that can bloom and grow to the extent that their green-coloured cells are visible both within and on top of water bodies…
Pathogenic microscopic organisms in source waters pose a risk to public health if water treatment plants do not remove them…
Cryptosporidium is a waterborne microscopic parasite with different forms at various stages of its lifecycle…