With ever increasing human and climate-related pressures on our precious water resources, sustainable management of our source waters and their catchments is crucial to enhancing our resilience as well as supporting the environment, economy, and health of our communities. Recent catchment management challenges experienced by our Members have ranged from changes to land use, urbanisation, population growth, and climate-related events. Degraded catchments place human and animal populations at risk and place additional pressures on water utilities to maintain the same level of water quality and service.
Our WaterRA Source and Catchments research projects aim to understand and inform the enhancement of a water supply within a catchment management area and the streams, rivers, dams, reservoirs, lakes, and boreholes within it. Stormwater harvesting systems in rural and remote areas that return water to a natural water body are also part of this catchment. As catchments play a huge role in enhancing liveability, the consideration of water and its use by the community for non-drinking purposes (e.g., recreation, commercial fishing, etc.) is also a research consideration.
Working with our members, WaterRA projects inform the ultimate enhancement of water bodies and their environment.
Featured project
Water utilities lack the information they need to implement risk-based adaptation and planning strategies that incorporate climate change…
Source and Catchments
These are all our current Source & Catchments projects

Extreme events can be unpredictable in terms of their impact on raw water quality which is further complicated by the possible introduction of contaminants of emerging concern (CECs) into catchment runoff…

The 2019-20 bushfire season in Australia was unprecedented in its extent, duration, intensity and impact on the natural environment and human livelihoods…
This project is investigating whether satellite remote sensing data can be used to calibrate the Integrated Water Quality Model, and to augment WaterNSW’s quantitative analysis of water quality parameters in drinking water catchments…
Waterborne pathogens cause millions of people to be sick each year globally, putting a burden on hospitals and having financial implications.

The overall aim of the study is to analyse the possible effects or influence that the different climatic drivers have on Lake Wivenhoe’s water levels….
This project will investigate the the fate and the sources of a range of priority emerging contaminants to CECs Australian wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs), that will allow water and environmental authorities better diagnostic tool for proactively managing the release of emerging contaminants into treatment plants…

This project aims to use qualitative and quantitative approaches, develop a consolidated time-based narrative (and / or) model showing how landscape change, interventions and social factors within the Moorabool catchment have impacted on the river’s health in terms of water quality, flow regimes, ecological carrying capacity, and bank stability / erosion…

This project aims to assess changes before and after completion of restoration works and in comparison to other nearby streams in…

The Australian water industry is currently focused on two VOCs, namely geosmin and MIB, which release an earthy-musty smell…

Sludge-drying lagoons are used in Australia as a convenient and cost-effective method of de-watering wastewater sludge…

It is well understood NOM character as well as concentration impacts its treatability by water treatment processes and that concentration and character can change over time…

To manage stormwater in an adaptive way as well as improving the mitigation strategies to cope with the climate change and urbanisation impacts, Water Sensitive Urban Design (WSUD) approaches are becoming popular…

Cyanobacterial blooms are a concern for water utilities due to the potential production of cyanotoxins and taste and odours…

This project explored the applicability of molecular approaches for taxonomic studies and rapid identification of invertebrates in a variety of freshwater habitats…
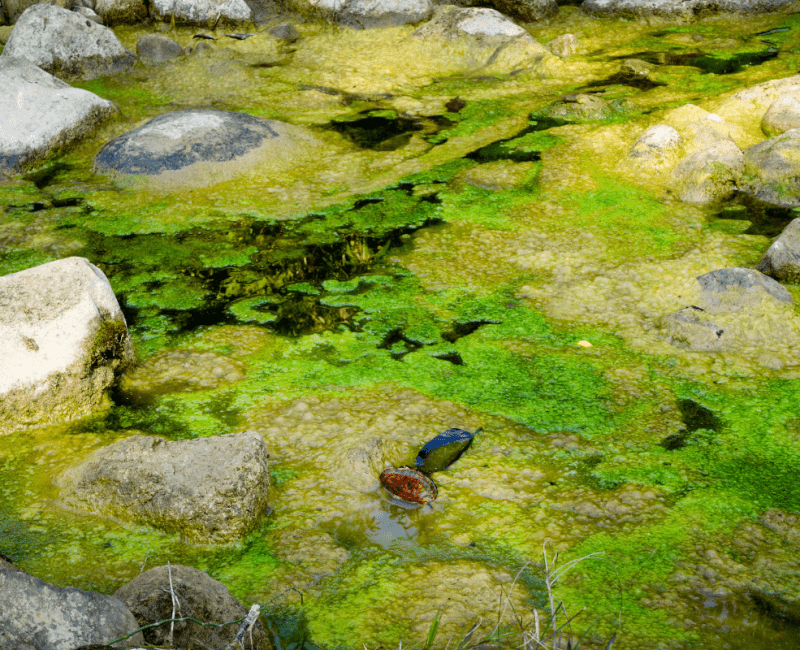

Detection of Algal and Cyanobacterial blooms have increased in lakes, rivers and reservoirs over the last two decades…

Increasing water demand due to a growing population and improved lifestyles is exerting greater pressure on existing water resources…

This project developed novel sampling tools to allow time integrated passive sampling of existing and emerging chemicals pollutants…

Lake hydrodynamic models are used by water utilities to provide an estimation of the conditions within a water storage…

Catchment health metrics are physical, chemical, biological, and socioeconomic indicators that collectively provide a holistic measure of a catchment’s state and functional capacity…

Source water protection underpins the safety and affordability of drinking water supplies where the prevention of water contamination provides greater surety than removal of contaminants…

The Stormwater Industry Association of Australia (SIA) formulated a draft Stormwater Quality Improvement Device Evaluation Protocol (SQIDEP) proposed for use in validation of stormwater treatment devices…

Blue-green algae reduce water quality, especially when they produce toxins…

The environmental conditions which cause blue-green algae (cyanobacteria) blooms vary according to location, the climate, and other attributes of aquatic ecosystems…
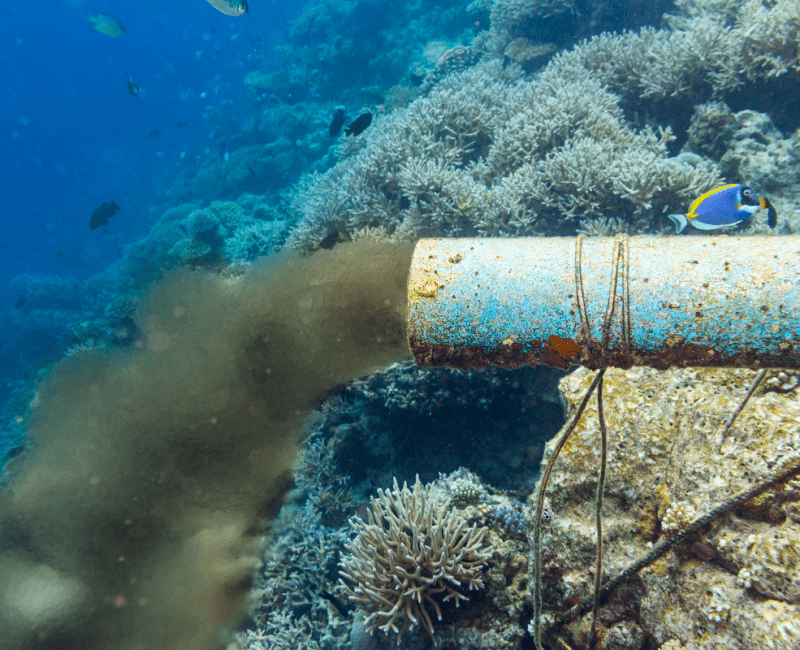

Every day, Australians produce ~5 billion litres of wastewater, which contains a cocktail of chemicals…
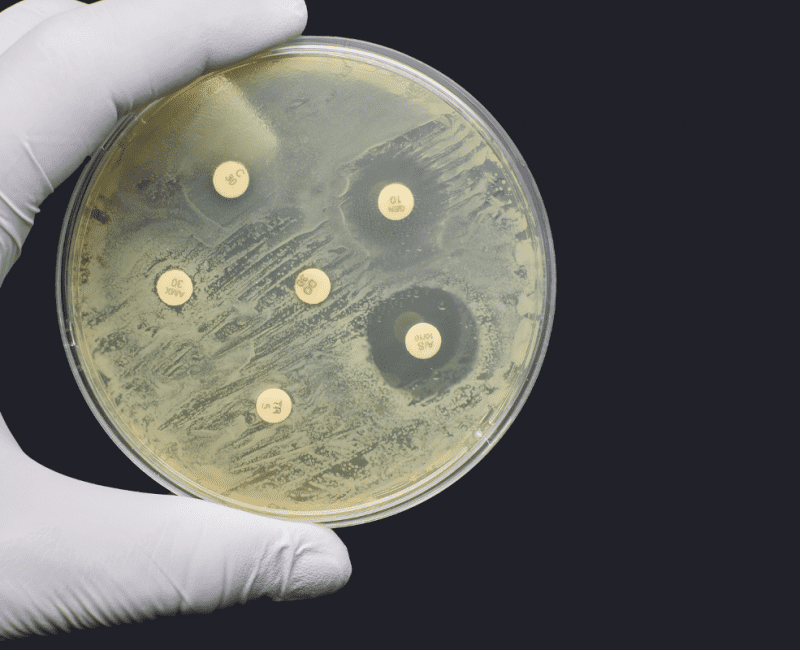
Significance of the environment as a reservoir for antimicrobial resistance from agricultural origin
Microscopic organisms such as fungi, bacteria and viruses can cause disease and infection, but most can be treated with pharmaceutical drugs…
Lakes and reservoirs are essential for water supply for humans and agriculture, and have an important role in flow regulation, biodiversity, and streamflow below dams…
Predicting the effects of climate change is a complicated business…
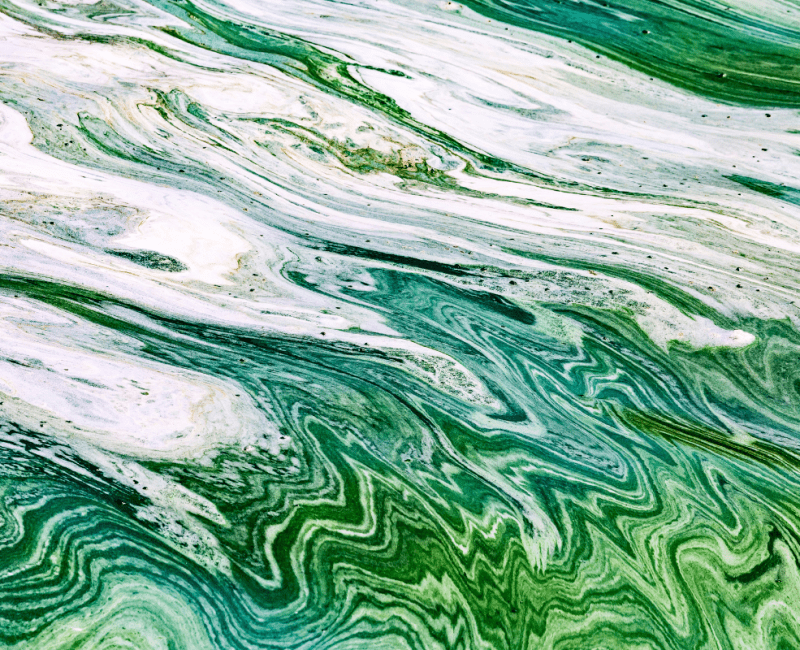

Blue-green algae (cyanobacteria) can bloom in marine and freshwater and cause additional problems for water utilities when they produce toxins and taste and odour compounds…

‘PFAS’ are a large class of chemical compounds, some of which can bioaccumulate or be toxic to humans and animals…

In an earlier project stormwater was collected from an urban environment, treated through electrolysis, injected into and retrieved from an acquifer, and reused for greywater irrigation…
Recycled stormwater has a range of possible uses that have different levels and types of human exposure…
A human hair is about 0.1mm wide, or 100 000 nanometres (nm); far too wide to qualify as a nanomaterial, which consists of particles, tubes and structures ranging from 1 to 100nm in size…
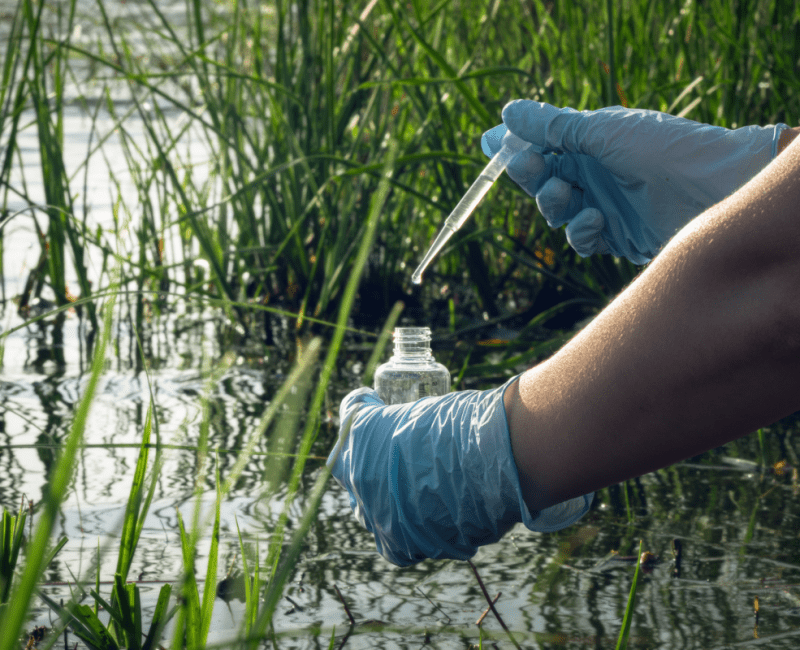

Fish, frogs, and other aquatic animals sometimes show signs of ‘endocrine disruption’; aberrant changes to their hormone or reproductive systems that are thought to be caused by chemicals in the water they inhabit…

Cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) which float in reservoirs have been studied for decades because when they bloom, the very high cell numbers cause a problem for water treatment plant (WTP) operators, who have to remove the cells, toxins, and taste and odour compounds they produce…

Blue-green algae (cyanobacteria) reduce water quality especially when they bloom and form high numbers of cells which produce toxins, and taste and odour compounds…

Water utilities lack the information they need to implement risk-based adaptation and planning strategies that incorporate climate change…

Groundwater, the main water supply in many remote areas of Australia, commonly contains 1500 mg/L or more ‘total dissolved solids’ (TDS), whereas palatable levels are 500 mg/L or less…
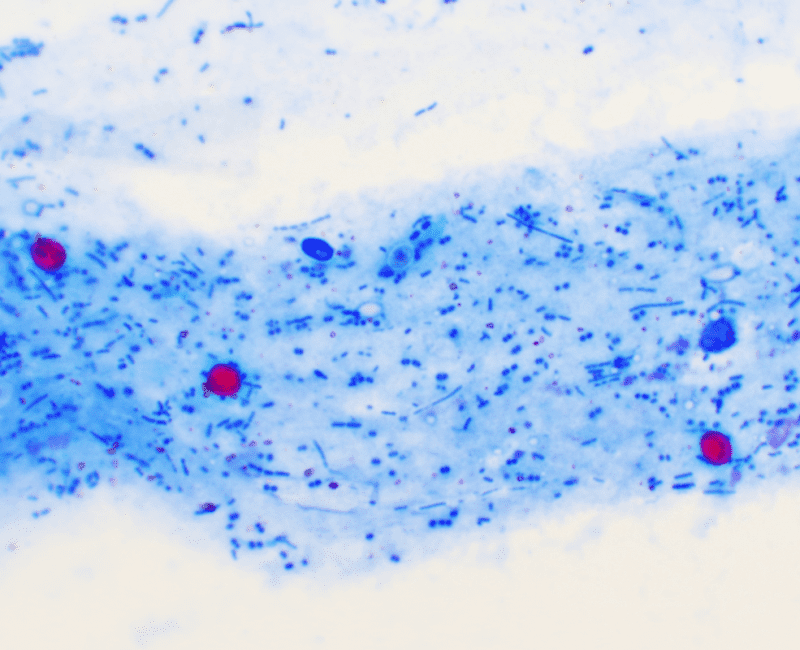
Cryptosporidium, a microscopic single-cell parasite, forms an “oocyst” with a resistant outer layer analogous to an eggshell…
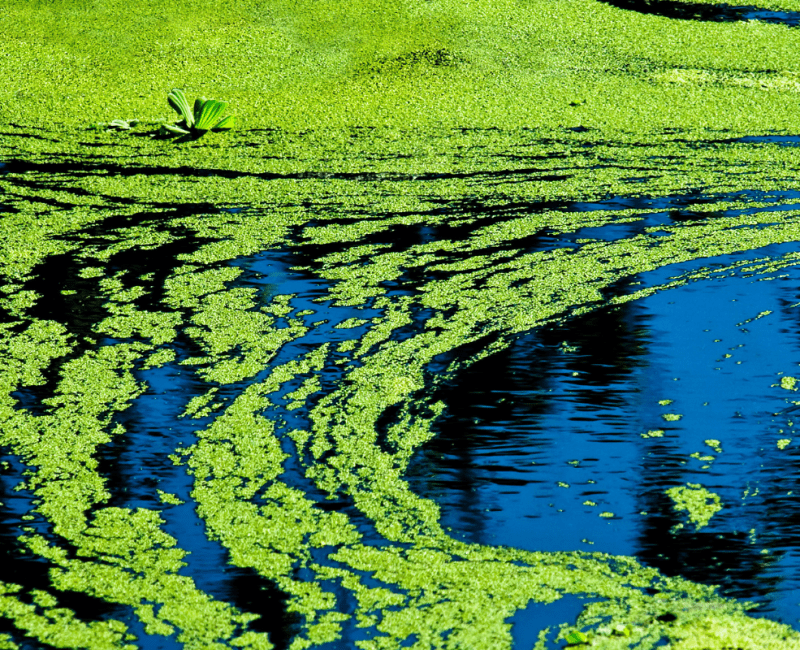

Cyanobacterial blooms in surface waters are a source of cells, taste and odour compounds, and a range of toxins…
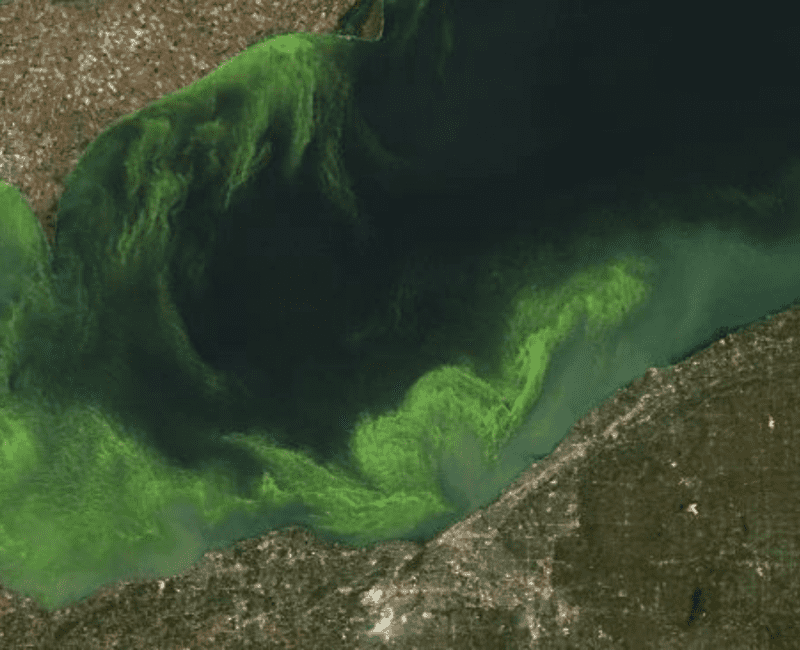

Cyanobacterial blooms are a major problem for reservoir managers because of the large numbers of cells and the toxins they contain…
This research has provided the most comprehensive account of the geographical distribution of blue-green algae (cyanobacteria), and the toxins they produce, in Australia…

This report on analysing the economic impact of harmful and nuisance algal blooms (HNABs) on the Australian water industry is the first effort in two decades to estimate their economic impact…
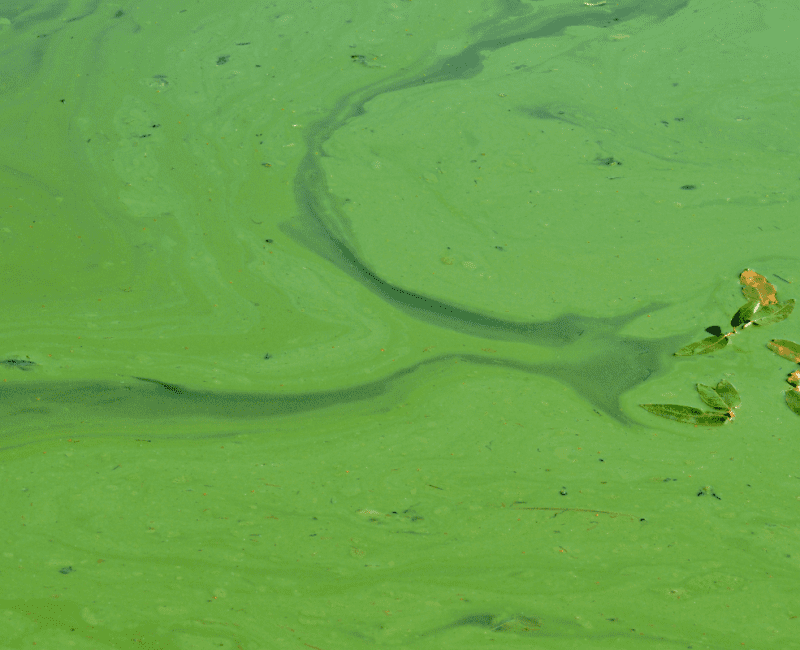

Blue-green algae are a nuisance, especially when they bloom and grow to high numbers in water storages and reservoirs…
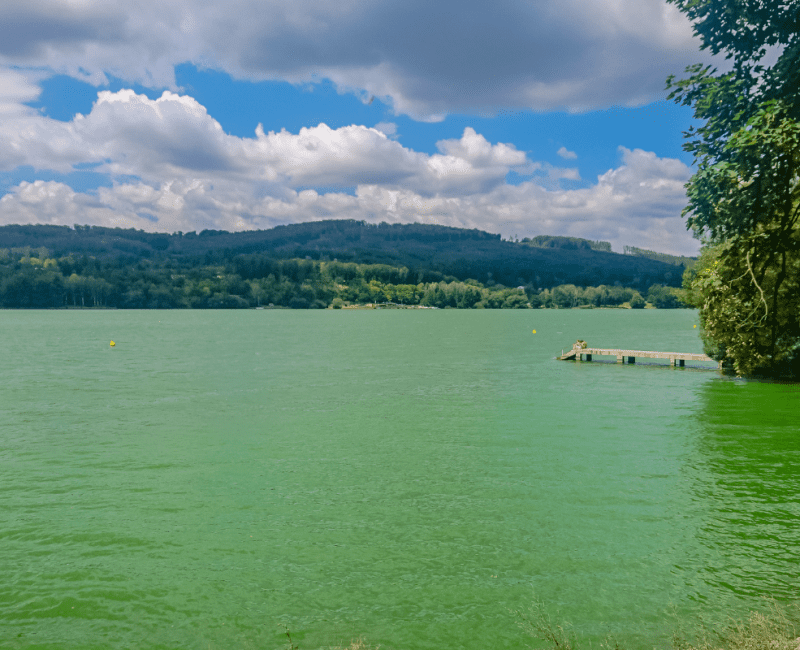
This research discusses various water quality risk management techniques and proposes a step-by-step catchment risk assessment methodology that is compatible with the Australian Drinking Water Guidelines…