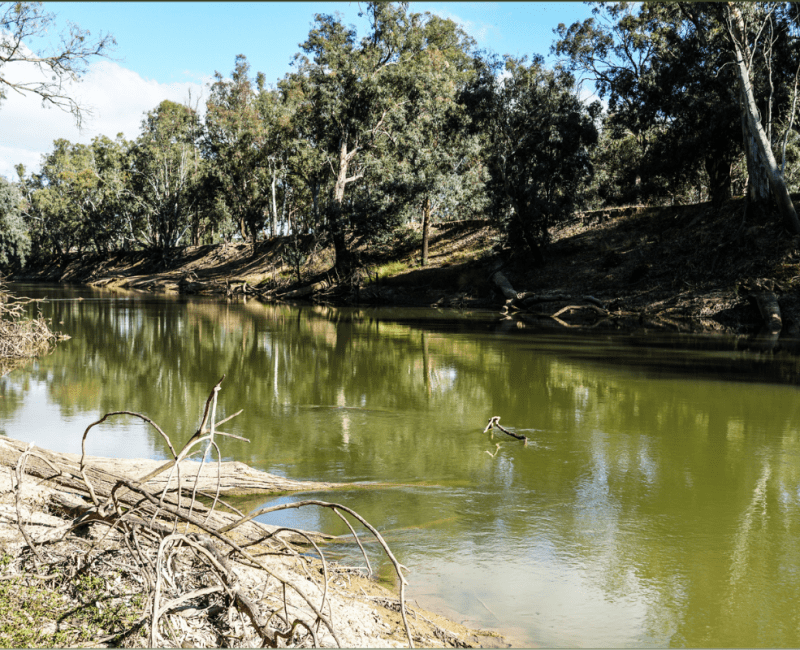

The environmental conditions which cause blue-green algae (cyanobacteria) blooms vary according to location, the climate, and other attributes of aquatic ecosystems…

The environmental conditions which cause blue-green algae (cyanobacteria) blooms vary according to location, the climate, and other attributes of aquatic ecosystems…
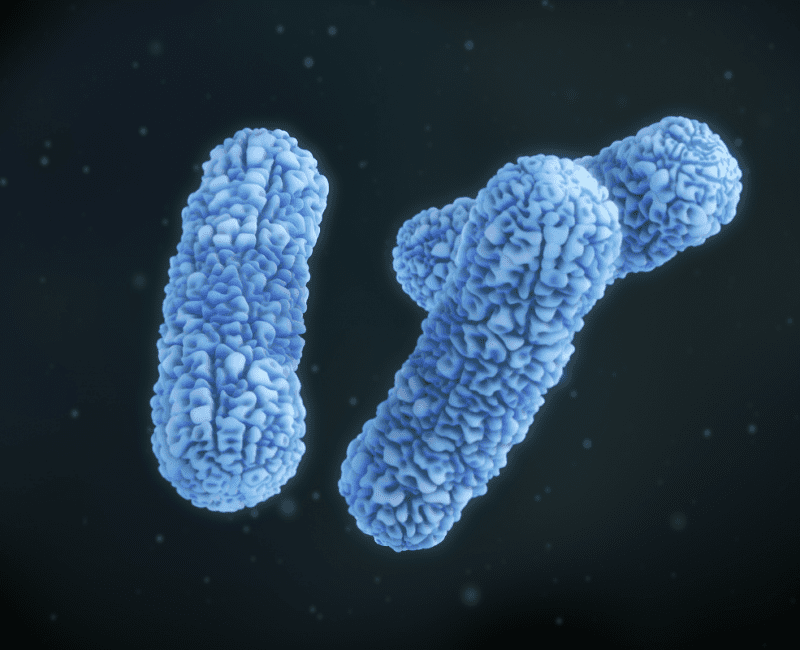
Burkholderia pseudomallei is a bacteria that is widespread in SE Asia and northern Australia, where there are an average of 16 cases per 100,000 people…

Water treatment plants (WTP) produce safe drinking water that does not contain harmful microscopic pathogens, but subsequent pipe-leaks or valve or hydrant malfunctions en route to the customers tap increase the risk of pathogens entering the public water supply…

Although a cluster of customer complaints can identify specific water quality issues such as a dirty water event, it is more difficult to understand the extent of general customer satisfaction with water quality and taste…

Water treatment plant operators remove cyanobacteria and the toxins they produce from source waters but calculating the amount of treatment needed for effective removal is difficult, particularly in bloom conditions when cyanobacterial cell numbers and toxins change quickly…

Microscopic pathogens in drinking water pose a risk to public health…

‘Microbial source tracking’ (MST) is a technique that aims to identify the animal that excreted faeces and polluted water…

Water utilities lack the information they need to implement risk-based adaptation and planning strategies that incorporate climate change…
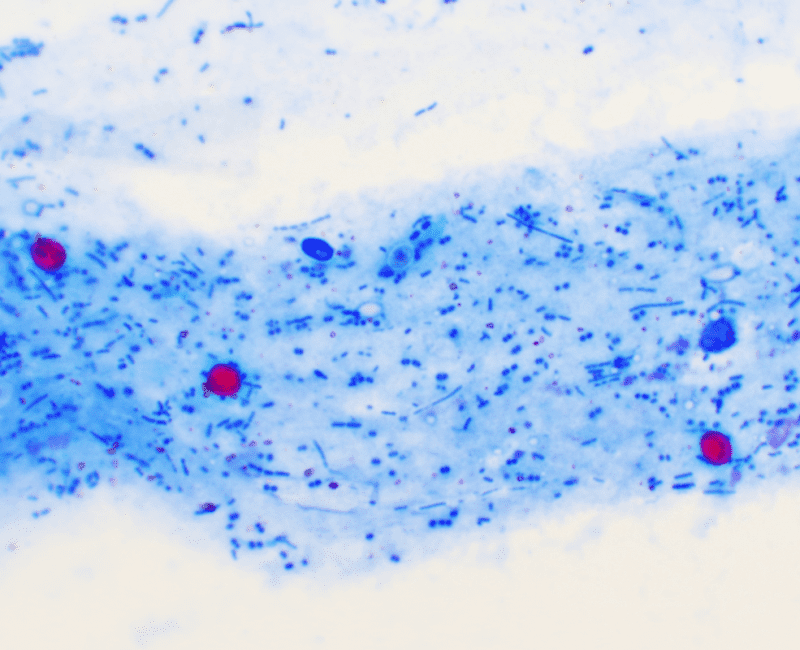
Cryptosporidium, a microscopic single-cell parasite, forms an “oocyst” with a resistant outer layer analogous to an eggshell…

The ADWG 2011 lacked objective, quantifiable criteria for measuring pathogen removal from source waters…