
Harmful pathogens and compounds must be removed from wastewater before it can be discharged to the environment or used for irrigation, and many source waters need salts removed to make them potable…

Harmful pathogens and compounds must be removed from wastewater before it can be discharged to the environment or used for irrigation, and many source waters need salts removed to make them potable…
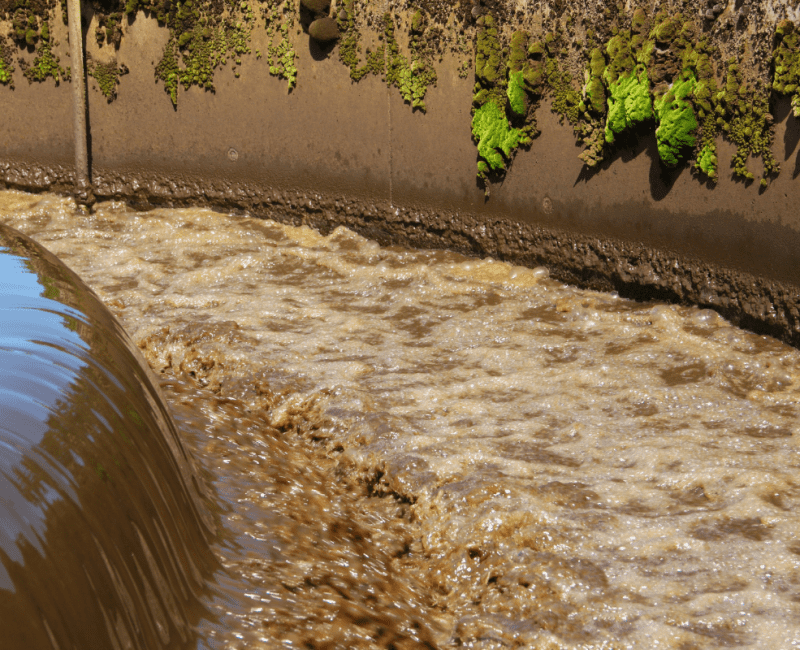

Sewage is delivered to wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) where benign microbial organisms within ‘activated sludge’ vessels contribute to the removal of harmful pathogens from the sewage…
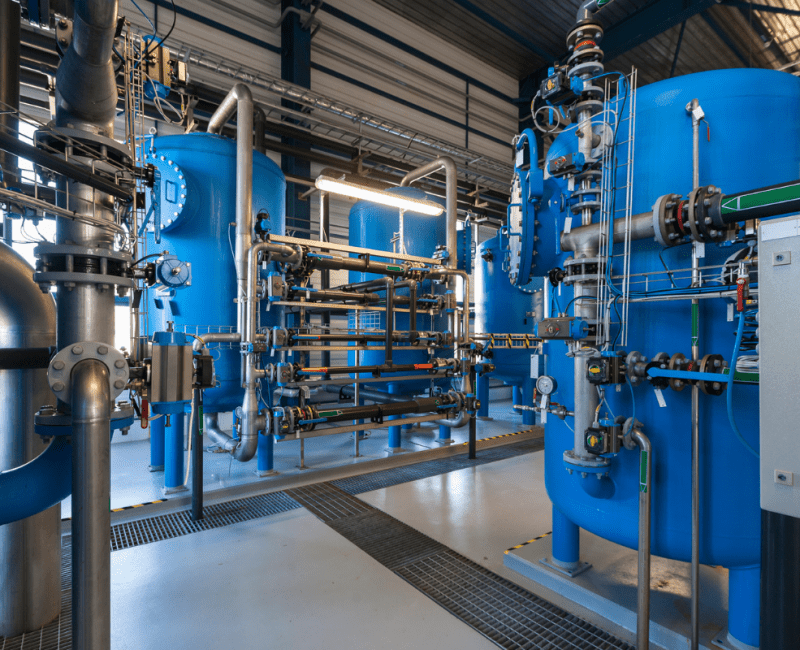

Although water utilities recognise the value of online instruments that provide real-time monitoring capability, there are problems with visualising and interpreting datasets, and with distinguishing between data resulting from real-world changes in treatment plant operating conditions, for example changed turbidity or flow, and instrument failure…
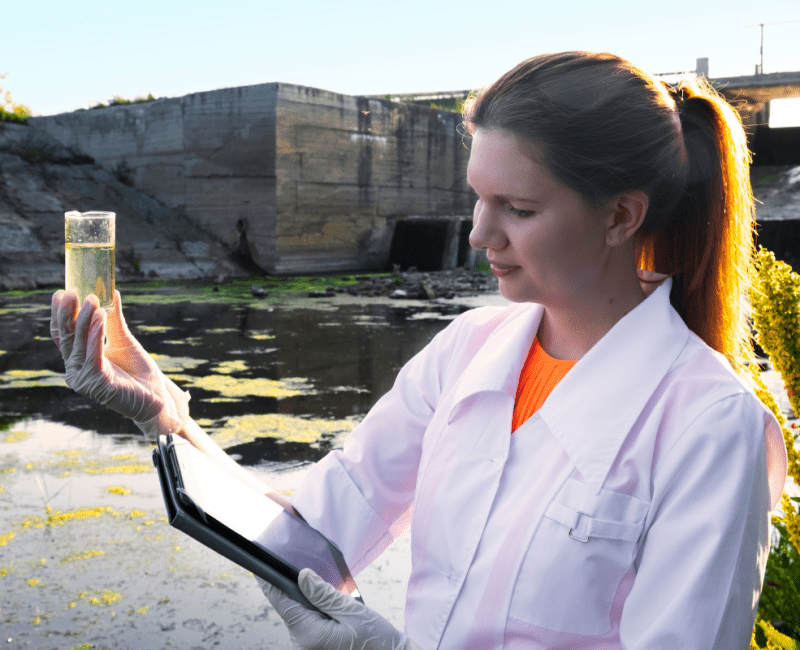

The ADWG has methods for predicting risks to water quality, but these were not developed for managing extreme climate-change driven weather events such as bushfires or floods…

Water utilities lack the information they need to implement risk-based adaptation and planning strategies that incorporate climate change…
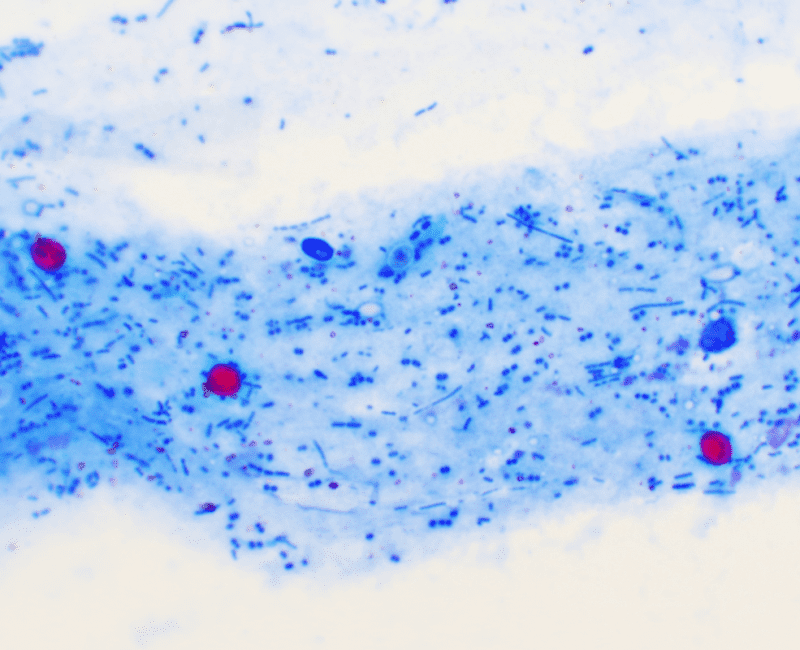
Cryptosporidium, a microscopic single-cell parasite, forms an “oocyst” with a resistant outer layer analogous to an eggshell…
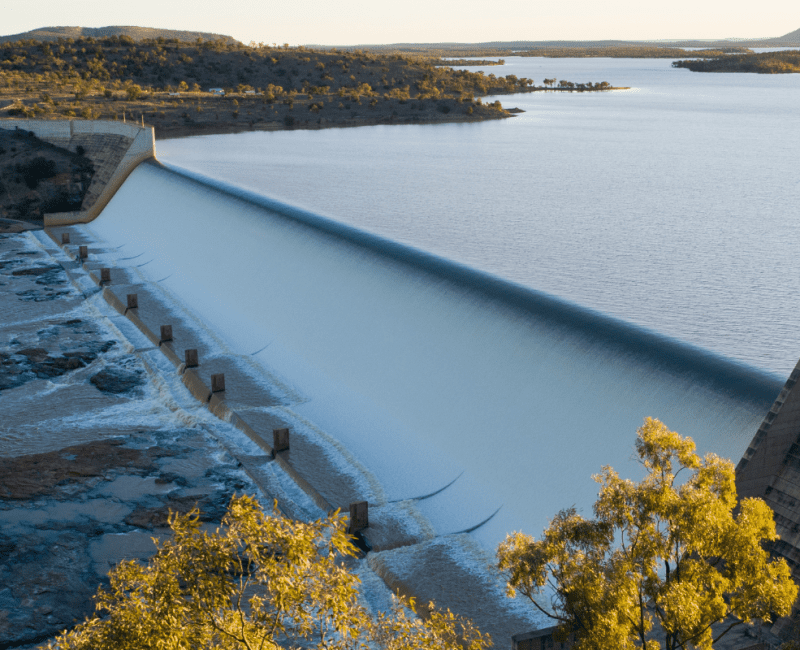

The ADWG 2011 lacked objective, quantifiable criteria for measuring pathogen removal from source waters…
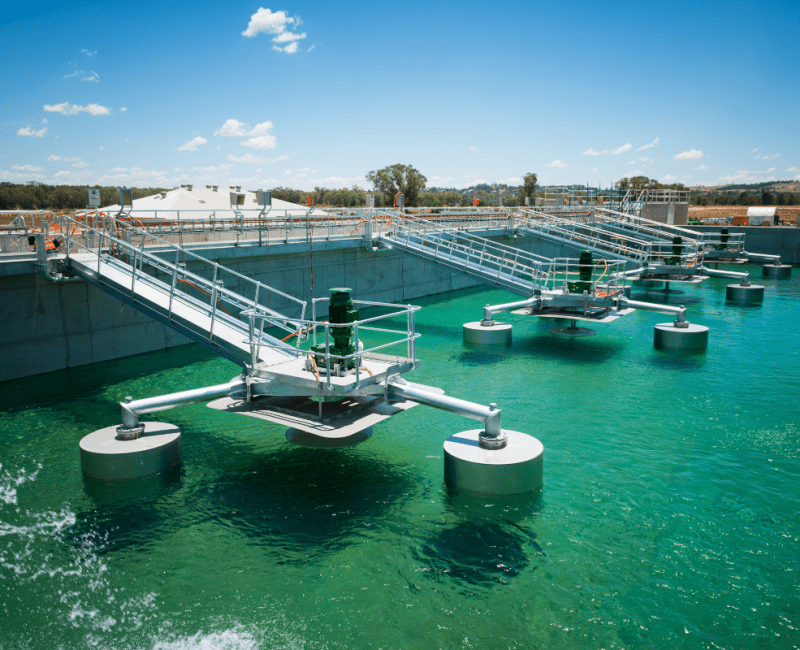
Water is disinfected to remove harmful organisms, then filtered and treated to remove contaminating pollutants…
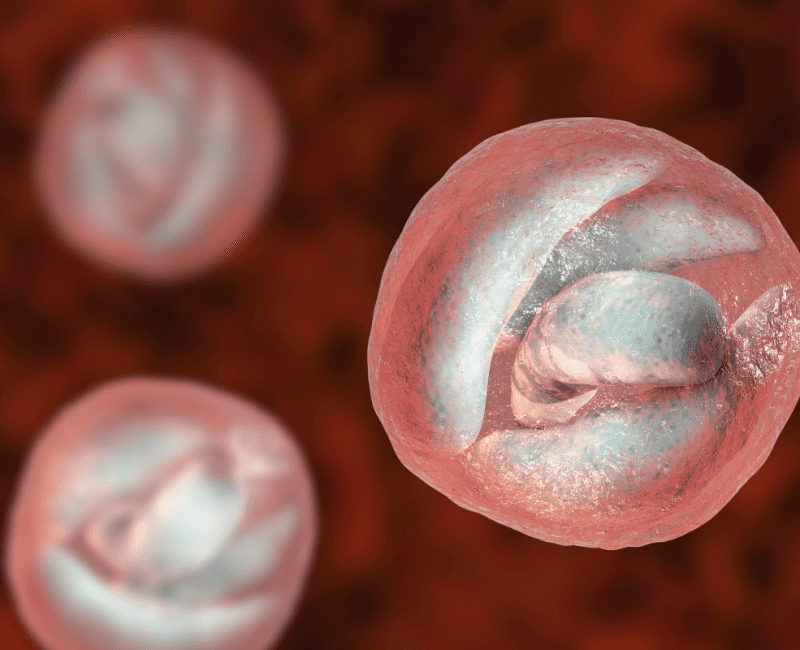
Cryptosporidium is a waterborne microscopic parasite with different forms at various stages of its lifecycle…