
Raw source water contains parts of plants, blue-green algae and their toxins, and many other types of organic matter…

Raw source water contains parts of plants, blue-green algae and their toxins, and many other types of organic matter…

Blue-green algae reduce water quality, especially when they produce toxins…

Although a cluster of customer complaints can identify specific water quality issues such as a dirty water event, it is more difficult to understand the extent of general customer satisfaction with water quality and taste…

Water treatment plant operators remove cyanobacteria and the toxins they produce from source waters but calculating the amount of treatment needed for effective removal is difficult, particularly in bloom conditions when cyanobacterial cell numbers and toxins change quickly…
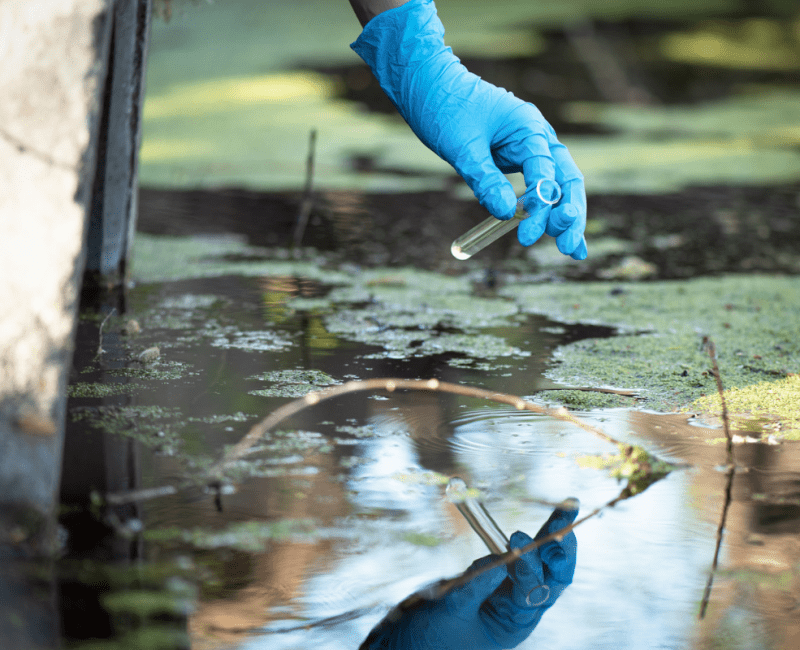

‘Microbial source tracking’ (MST) is a technique that aims to identify the animal that excreted faeces and polluted water…
Cryptosporidium, a microscopic pathogen, forms infectious oocysts which are removed by specific and targeted water treatments…

Components of dissolved organic matter (DOM) and dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) in source waters can react with disinfecting chlorine or chloramine to form nitrogenous disinfection byproducts (n-DBPs) which might be toxic and hazardous to health…
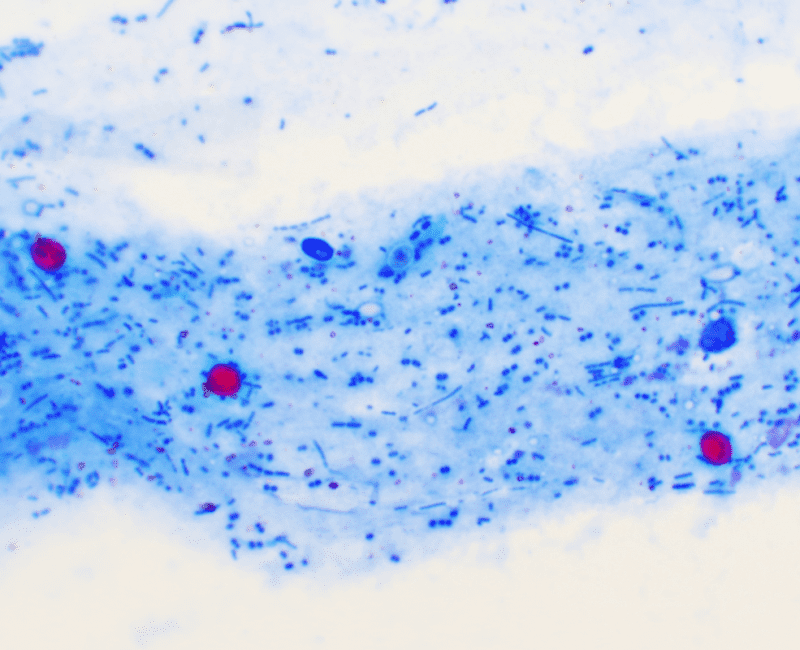
Cryptosporidium, a microscopic single-cell parasite, forms an “oocyst” with a resistant outer layer analogous to an eggshell…
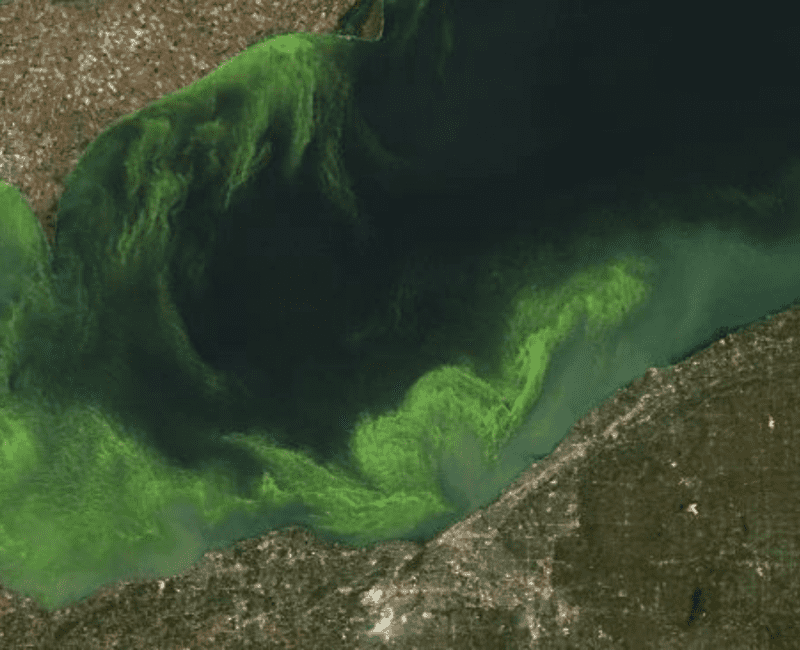

Cyanobacterial blooms are a major problem for reservoir managers because of the large numbers of cells and the toxins they contain…
This research has provided the most comprehensive account of the geographical distribution of blue-green algae (cyanobacteria), and the toxins they produce, in Australia…