
Blue-green algae (cyanobacteria) reduce water quality especially when they bloom and form high numbers of cells which produce toxins, and taste and odour compounds…

Blue-green algae (cyanobacteria) reduce water quality especially when they bloom and form high numbers of cells which produce toxins, and taste and odour compounds…

This research was prompted by concerns that rooftop-harvested rainwater fed into household hot water services might expose the public to harmful pathogens such as salmonella…

Groundwater, the main water supply in many remote areas of Australia, commonly contains 1500 mg/L or more ‘total dissolved solids’ (TDS), whereas palatable levels are 500 mg/L or less…
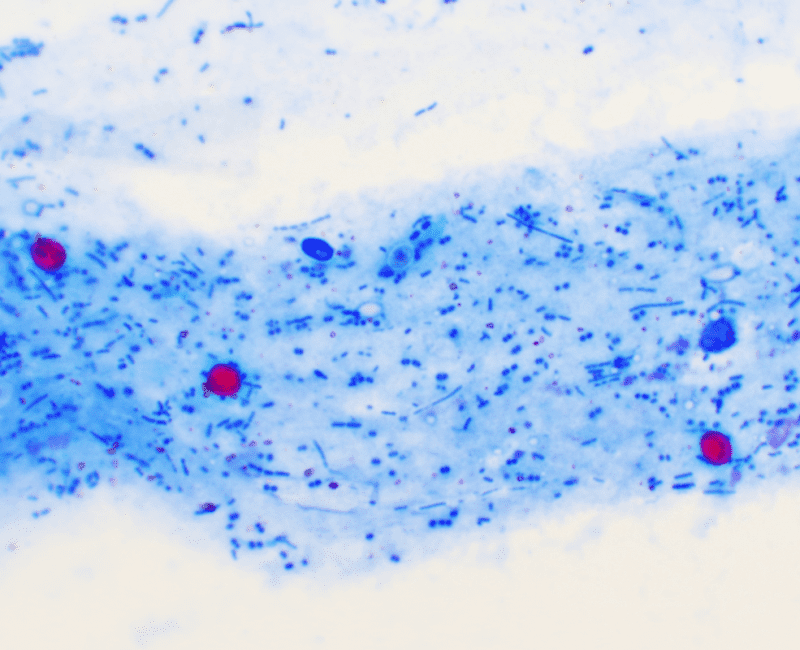
Cryptosporidium, a microscopic single-cell parasite, forms an “oocyst” with a resistant outer layer analogous to an eggshell…

The ADWG 2011 lacked objective, quantifiable criteria for measuring pathogen removal from source waters…

Chlorine removes harmful pathogens from water but has the disadvantage of forming disinfection by-products (DBPs) by reacting with organic matter sometimes found in water…
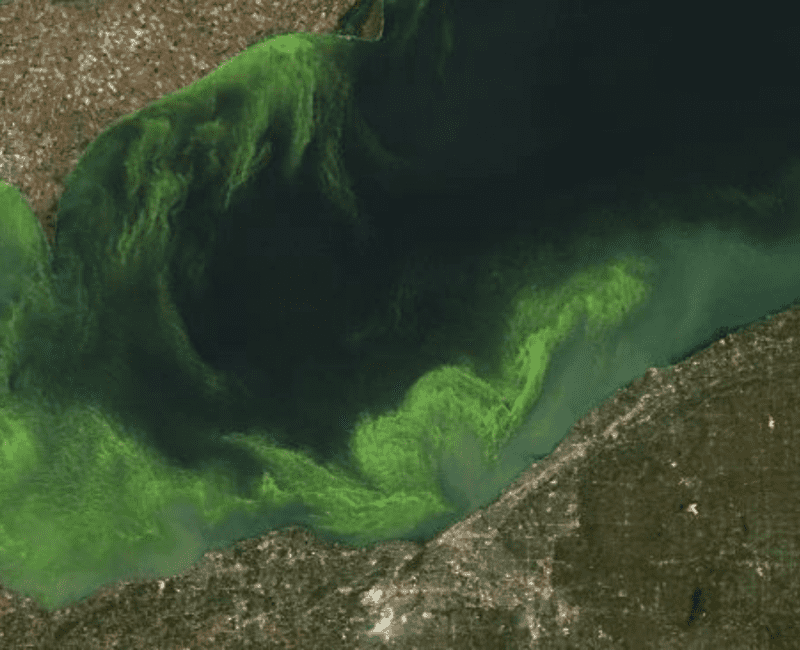

Cyanobacterial blooms are a major problem for reservoir managers because of the large numbers of cells and the toxins they contain…
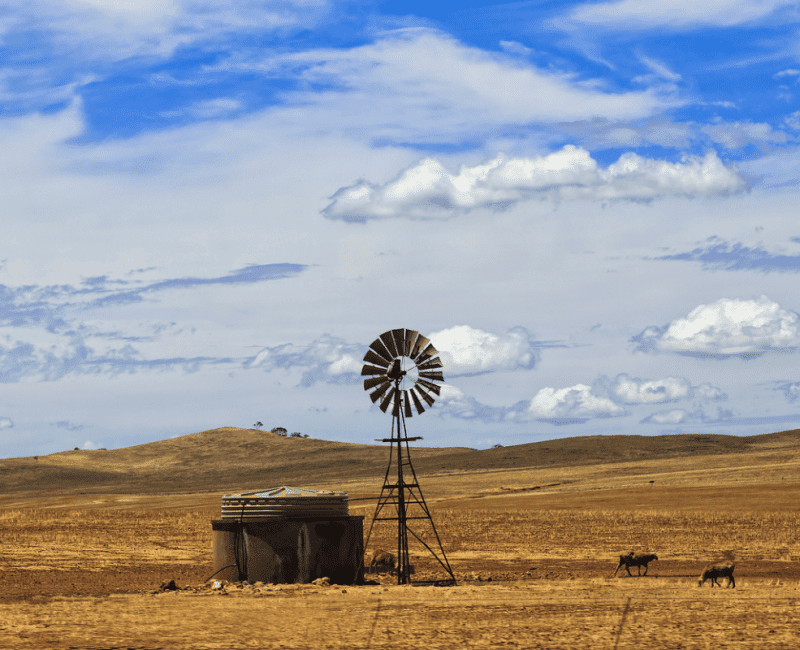

Remote and regional Australian communities commonly produce potable water by removing salt from brackish groundwater…

Climate change is depleting water resources, while population increases drive demand for additional recreational facilities, particularly in the vicinity of urban centres…

Approximately 11% of Australians use rainwater as their main source of potable water but this poses a potential health risk caused by chemical contaminants or microbial pathogens from birds or mammals being washed off the roof…